Introduction
When choosing a reliable Virtual private server solution, many website owners decide based on pricing and specifications but most often ignore virtualization technology.
Choosing a virtualization technology could be the difference between having a high performance and a poor application.
Thus, it is very important to understand what virtualization is and the different kinds of virtualization technology available to make good decisions whenever you need a VPS.
In this article, we’ll go through everything you need to know about Linux KVM and Linux OpenVZ including their differences and best use case scenario.
But first,
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of something, such as an operating system, application, storage device, or network resource.
Virtualization allows one physical resource to be divided into multiple logical resources, each of which can be used independently.
Virtualization can be used to improve the efficiency and utilization of hardware, by allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical computer.
It can also be used to improve security, by isolating different systems and applications in separate virtual machines.
What is a Hypervisor?
A hypervisor is a piece of software (or hardware in some cases) that makes virtualization possible, its main function is to divide and assign hardware and OS resources across instances of Virtual machines.
A hypervisor makes it possible to set resources such as memory, storage, CPU power, and network bandwidth for any Virtual Machine created.
It can also be used to stop, restart, and destroy existing virtual machines on demand.
Both KVM & Open VZ are Hypervisors used by hosting providers to segment and create tiers of servers and share resources from one or a set of physical hardware.
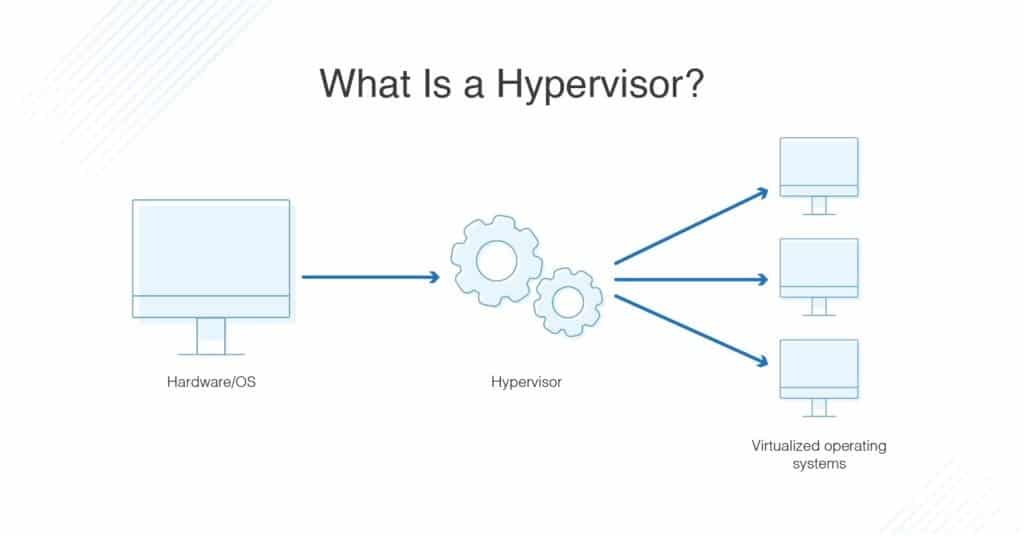
Source: https://www.dnsstuff.com/what-is-hypervisor
Each Hypervisor has certain advantages over the other as well as disadvantages depending on the use case.
Linux KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)
It translates to Kernel Virtual Machine an open-source hypervisor that lets you create and run multiple operating systems on a single computer (using a type 2 hypervisor).
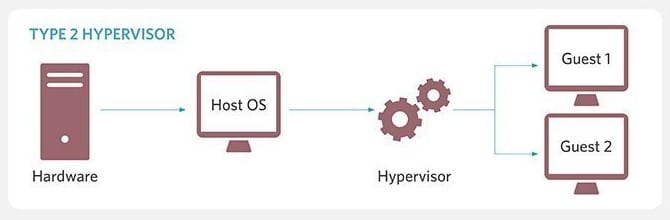
Each operating system instance created is called a virtual machine (with its separate dedicated kernel).
It is mainly used for creating virtual machines with Linux as their OS but supports other guest operating systems like Windows, Haiku, and Solaris.
Having been around for more than a decade, it is used by major companies like Google, Amazon, and Facebook.
Features:
Hardware Virtualization:
It harnesses hardware-assisted virtualization, allowing virtual machines (VMs) to directly access physical hardware resources. This minimizes the overhead associated with traditional software-based virtualization, resulting in exceptional performance and efficiency for resource-intensive workloads.
Multi-OS Support:
It boasts broad compatibility with various guest operating systems, encompassing Linux distributions, Windows, and more. This versatility enables users to simultaneously run multiple OS instances on a single host, catering to diverse application and software requirements within the virtual environment.
Live Migration:
It empowers live migration, permitting the seamless transfer of running VMs from one physical host to another without service interruption. This feature optimizes resource allocation, facilitates load balancing, and enhances fault tolerance, ensuring continuous operations in virtualized environments.
Snapshot and Cloning:
It offers convenient snapshot and cloning capabilities, enabling users to create point-in-time copies of VMs and replicate them swiftly. This functionality streamlines backup processes, facilitates testing and development, and expedites the deployment of new VM instances.
Security:
It prioritizes security with features like SELinux integration and virtualization-based security. Isolating VMs and implementing security measures at the hypervisor level, it helps safeguard virtualized environments, protecting them from potential threats and unauthorized access.
OpenVz (Open Virtuozzo)
It is an OS-level virtualization technology that allows multiple isolated operating systems (OSes) to run on a single physical server. Each OS is called a container and is equivalent to a virtual machine (VM) for Kernel Virtual Machine.
Containers, however, are much more lightweight and efficient than VMs, making them better suited for hosting multiple applications on a single server.
All containers you construct with Open Virtuozzo share one single host kernel, which is packaged as a Linux distribution. As a result, it does not have support for other operating systems.
It is also an open-source project and is free for anyone to use.
What is the difference between KVM and OpenVZ?
The key difference between KVM and OpenVZ lies in the way they handle virtualization.
OpenVZ handles virtualization at an operating system level while KVM handles virtualization at a full or hardware level.
Since Kernel Virtual Machine’s virtualization is at a hardware level, it is better able to completely isolate each virtual machine thus why it can support other operating systems and can be customizable to almost any length.
Open Virtuozzo uses OS-level virtualization which essentially means all containers created must be Linux-based and share the same resources from the host’s kernel, this makes it less customizable and more specialized for Linux-based applications.
The Virtual Machines created with KVM use the physical machine hardware resources directly which does have a lot of performance advantages over OpenVZ which relies on the host’s kernel.
The downside to Kernel Virtual Machine virtual machines is the fact that they have high overhead which essentially means high running costs.
Compared to Kernel Virtual Machine, OpenVZ containers can run with little overhead on their host’s resources since they don’t require a full-fledged hypervisor and depend solely on the host whose Hypervisor is kernel-based.
Also with OpenVZ, you have greater control over resource distribution with as much as 99% of physical hardware being assignable to containers.
For example, when physical memory (RAM) is not being used in an OpenVZ setup, it is available for any of the running containers to access.
If any of the containers decides to run processes that are RAM intensive, it will affect the overall performance of the entire container network (very common when too many containers are created).
For KVM, each virtual machine is created with hard limits which essentially means they can never use more than what is assigned to them even if there is extra unused memory lying around.
Both are completely free to use but when it comes to operating costs, KVM is more expensive, has a higher hardware requirement to operate, and requires a complicated setup.
This makes OpenVZ a favorite choice for companies on a budget and Kernel-based Virtual Machine is better suited for larger enterprises that require more abstraction and isolation.
FAQ
Is KVM faster than OpenVZ?
Kernel virtual machines access the machine’s physical resources almost natively thus giving them a greater speed when compared to OpenVZ containers that require a middleware (the host’s kernel) to access resources.
Can I run Windows inside an OpenVZ container?
No, and this is simply because it is bundled with the Linux kernel and since it handles virtualization at an OS level, every container created must be based on the same Operating system, and in this case, that would be Linux.
What is The Key difference Between KVM and OpenVZ?
Linux KVM and OpenVZ are both types of virtualization software, but they have some key differences. OpenVZ creates containers that share a single kernel, while Kernel Virtual Machine uses virtual machines with their kernels. This means that KVM is better for hosting multiple operating systems, while OpenVZ is better for hosting multiple applications.
Conclusion
Linux KVM vs OpenVZ are both popularly used virtualization technologies that allow you to run multiple operating systems on a single server.
In this article, we break down the features of each virtualization technology and concisely explain the key differences between them.
After reading this article, you should be able to know exactly which of these two technologies you need based on a use case.
We hope you found this article useful.

Leave a Reply